Search any question & find its solution
Question:
Answered & Verified by Expert
A box of mass $3 \mathrm{~kg}$ moves on a horizontal frictionless table and collides with another box of mass $3 \mathrm{~kg}$ initially at rest on the edge of the table at height $1 \mathrm{~m}$. The speed of the moving box just before the collision is $4 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$. The two boxes stick together and fall from the table. The kinetic energy just before the boxes strike the floor is (Assume, acceleration due to gravity, $g=10 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}^2$ )
Options:
Solution:
1169 Upvotes
Verified Answer
The correct answer is:
$72 \mathrm{~J}$
$$
\text { The given situation can be shown as below, }
$$
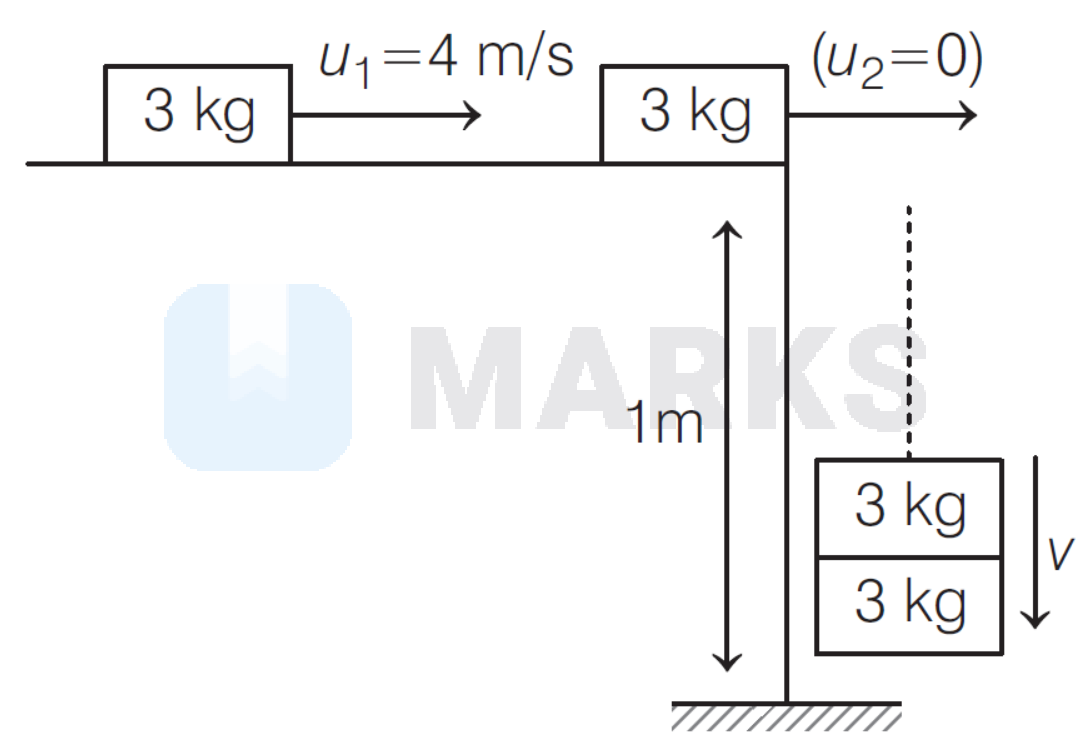
According to law of conservation of momentum, total momentum before collision $=$ total momentum after collision.
$$
m_1 u_1+m_2 u_2=\left(m_1+m_2\right) v
$$
Given, mass of boxes, $\quad m_1=m_2=3 \mathrm{~kg}$
speed of the moving box, $\quad u_2=4 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$ and initial speed of second box, $u_2=0$ Putting the given values, we get
$$
\Rightarrow \quad \begin{aligned}
& 3 \times 4+3 \times 0=(3+3) v \\
& \quad v=\frac{12}{6}=2 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}
\end{aligned}
$$
Thus, the two bodies move with the velocity of $2 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$. Applying law of conservation of energy at height of $1 \mathrm{~m}$ and at the bottom of table.
$$
\mathrm{KE}_2+\mathrm{PE}_2=\mathrm{KE}_2+\mathrm{PE}_2
$$
At the bottom just above the ground, the total energy is $\mathrm{KE}$ as height is approximately equals to zero.
$$
\begin{aligned}
& \frac{1}{2}\left(m_1+m_2\right) v^2+\left(m_1+m_2\right) g h=\mathrm{KE}_2 \\
& \Rightarrow \quad \mathrm{KE}_2=\frac{1}{2} \times 6 \times 4+6 \times 10 \times 1 \\
&=12+60=72 \mathrm{~J}
\end{aligned}
$$
Hence, the kinetic energy just before the boxes strike the floor is $72 \mathrm{~J}$.
\text { The given situation can be shown as below, }
$$

According to law of conservation of momentum, total momentum before collision $=$ total momentum after collision.
$$
m_1 u_1+m_2 u_2=\left(m_1+m_2\right) v
$$
Given, mass of boxes, $\quad m_1=m_2=3 \mathrm{~kg}$
speed of the moving box, $\quad u_2=4 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$ and initial speed of second box, $u_2=0$ Putting the given values, we get
$$
\Rightarrow \quad \begin{aligned}
& 3 \times 4+3 \times 0=(3+3) v \\
& \quad v=\frac{12}{6}=2 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}
\end{aligned}
$$
Thus, the two bodies move with the velocity of $2 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$. Applying law of conservation of energy at height of $1 \mathrm{~m}$ and at the bottom of table.
$$
\mathrm{KE}_2+\mathrm{PE}_2=\mathrm{KE}_2+\mathrm{PE}_2
$$
At the bottom just above the ground, the total energy is $\mathrm{KE}$ as height is approximately equals to zero.
$$
\begin{aligned}
& \frac{1}{2}\left(m_1+m_2\right) v^2+\left(m_1+m_2\right) g h=\mathrm{KE}_2 \\
& \Rightarrow \quad \mathrm{KE}_2=\frac{1}{2} \times 6 \times 4+6 \times 10 \times 1 \\
&=12+60=72 \mathrm{~J}
\end{aligned}
$$
Hence, the kinetic energy just before the boxes strike the floor is $72 \mathrm{~J}$.
Looking for more such questions to practice?
Download the MARKS App - The ultimate prep app for IIT JEE & NEET with chapter-wise PYQs, revision notes, formula sheets, custom tests & much more.