Search any question & find its solution
Question:
Answered & Verified by Expert
A particle falling vertically from a height hits a plane surface inclined to horizontal at an angle $\theta$ with speed $v_0$ and rebounds elastically. Find the distance along the plane where it will hit second time.
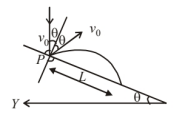

Solution:
2422 Upvotes
Verified Answer
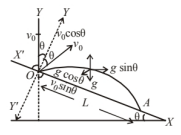
From the given figure,
$$
\begin{aligned}
&v_x=v_0 \sin \theta \text { and } v_y=v_0 \cos \theta \\
&g_x=g \sin \theta, g_y=-g \cos \theta
\end{aligned}
$$
Consider the motion of the projectile from $O$ to $\mathrm{A}$ in new YOY' axis.
$$
\begin{aligned}
&s_y=0, u_y=v_0 \cos \theta \\
&a_y=-g \cos \theta \text { (upward) } \\
&t=T \text { (time of flight) }
\end{aligned}
$$
Applying equation of kinematics,
$$
\begin{aligned}
&s_y=u_y t+\frac{1}{2} a_y t^2 \\
&0=v_0 \cos \theta T+\frac{1}{2}(-g \cos \theta) T^2 \\
&(T=0) \text { or }\left[v_0 \cos \theta-\frac{g \cos \theta T}{2}\right]=0 \\
&T=\frac{2 v_0 \cos \theta}{g \cos \theta}
\end{aligned}
$$
As $T=0$, corresponds to point $O$.
Hence, $T=\frac{2 v_0}{g}$
Now considering motion along $O X$ axis
$$
s_x=L, u_x=v_0 \sin \theta, a_x=g \sin \theta, t=T=\frac{2 v_0}{g}
$$
Applying equation of kinematics,
$$
\begin{aligned}
s &=u_x t+\frac{1}{2} a_x t^2 \\
L &=v_0 \sin \theta t+\frac{1}{2} g \sin \theta t^2 \\
&=\left(v_0 \sin \theta\right)(T)+\frac{1}{2} g \sin \theta T^2 \\
&=\left(v_0 \sin \theta\right)\left(\frac{2 v_0}{g}\right)+\frac{1}{2} g \sin \theta \times\left(\frac{2 v_0}{g}\right)^2
\end{aligned}
$$
$\begin{aligned}=& \frac{2 v_0^2}{g} \sin \theta+\frac{1}{2} g \sin \theta \times \frac{4 v_0^2}{g^2} \\=& \frac{2 v_0^2}{g}[\sin \theta+\sin \theta] \\ L &=\frac{4 v_0^2}{g} \sin \theta \end{aligned}$
$$
\begin{aligned}
&v_x=v_0 \sin \theta \text { and } v_y=v_0 \cos \theta \\
&g_x=g \sin \theta, g_y=-g \cos \theta
\end{aligned}
$$
Consider the motion of the projectile from $O$ to $\mathrm{A}$ in new YOY' axis.

$$
\begin{aligned}
&s_y=0, u_y=v_0 \cos \theta \\
&a_y=-g \cos \theta \text { (upward) } \\
&t=T \text { (time of flight) }
\end{aligned}
$$
Applying equation of kinematics,
$$
\begin{aligned}
&s_y=u_y t+\frac{1}{2} a_y t^2 \\
&0=v_0 \cos \theta T+\frac{1}{2}(-g \cos \theta) T^2 \\
&(T=0) \text { or }\left[v_0 \cos \theta-\frac{g \cos \theta T}{2}\right]=0 \\
&T=\frac{2 v_0 \cos \theta}{g \cos \theta}
\end{aligned}
$$
As $T=0$, corresponds to point $O$.
Hence, $T=\frac{2 v_0}{g}$
Now considering motion along $O X$ axis
$$
s_x=L, u_x=v_0 \sin \theta, a_x=g \sin \theta, t=T=\frac{2 v_0}{g}
$$
Applying equation of kinematics,
$$
\begin{aligned}
s &=u_x t+\frac{1}{2} a_x t^2 \\
L &=v_0 \sin \theta t+\frac{1}{2} g \sin \theta t^2 \\
&=\left(v_0 \sin \theta\right)(T)+\frac{1}{2} g \sin \theta T^2 \\
&=\left(v_0 \sin \theta\right)\left(\frac{2 v_0}{g}\right)+\frac{1}{2} g \sin \theta \times\left(\frac{2 v_0}{g}\right)^2
\end{aligned}
$$
$\begin{aligned}=& \frac{2 v_0^2}{g} \sin \theta+\frac{1}{2} g \sin \theta \times \frac{4 v_0^2}{g^2} \\=& \frac{2 v_0^2}{g}[\sin \theta+\sin \theta] \\ L &=\frac{4 v_0^2}{g} \sin \theta \end{aligned}$
Looking for more such questions to practice?
Download the MARKS App - The ultimate prep app for IIT JEE & NEET with chapter-wise PYQs, revision notes, formula sheets, custom tests & much more.