Search any question & find its solution
Question:
Answered & Verified by Expert
A pendulum has length of $0.4 \mathrm{~m}$ and maximum speed $4 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$. When the length makes
an angle $30^{\circ}$ with the horizontal, its speed will be
$\left[\sin \frac{\pi}{6}=\cos \frac{\pi}{3}=0 \cdot 5\right.$ and $\left.\mathrm{g}=10 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}^{2}\right]$
Options:
an angle $30^{\circ}$ with the horizontal, its speed will be
$\left[\sin \frac{\pi}{6}=\cos \frac{\pi}{3}=0 \cdot 5\right.$ and $\left.\mathrm{g}=10 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}^{2}\right]$
Solution:
1486 Upvotes
Verified Answer
The correct answer is:
$2 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$
A pendulum has length of $0.4 \mathrm{~m}$ and maximum speed $4 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$. When the length makes an angle $30^{\circ}$ with the horizontal, its speed will be $2 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$.
Explanation:
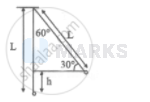
$h=L-L \cos 0=L(1-\cos \theta)$
$=0.4\left(1-\cos 60^{\circ}\right)$
$=0.4\left(1-\frac{1}{2}\right)$
$=0.4 \times \frac{1}{2}$
$=0.2$
$\frac{1}{2} m v_{1}^{2}=\frac{1}{2} m v_{2}^{2}+m g h$
$v_{1}^{2}=v_{2}^{2}+2 g h$
$\therefore v_{2}^{2}=v_{1}^{2}-2 g h$
$=(4)^{2}-2 \times 10 \times 0.2$
$=16-4=12$
$\therefore v_{2}=\sqrt{12}=2 \sqrt{3} m / s$
Explanation:

$h=L-L \cos 0=L(1-\cos \theta)$
$=0.4\left(1-\cos 60^{\circ}\right)$
$=0.4\left(1-\frac{1}{2}\right)$
$=0.4 \times \frac{1}{2}$
$=0.2$
$\frac{1}{2} m v_{1}^{2}=\frac{1}{2} m v_{2}^{2}+m g h$
$v_{1}^{2}=v_{2}^{2}+2 g h$
$\therefore v_{2}^{2}=v_{1}^{2}-2 g h$
$=(4)^{2}-2 \times 10 \times 0.2$
$=16-4=12$
$\therefore v_{2}=\sqrt{12}=2 \sqrt{3} m / s$
Looking for more such questions to practice?
Download the MARKS App - The ultimate prep app for IIT JEE & NEET with chapter-wise PYQs, revision notes, formula sheets, custom tests & much more.