Search any question & find its solution
Question:
Answered & Verified by Expert
A rod $A B$ of length $1 \mathrm{~m}$ is placed at the edge of a smooth table as shown. It is hit horizontally at point $B$. If the displacement of centre of mass in 1s is $5 \sqrt{2} \mathrm{~m}$, then the angular velocity of the rod is (Take, $g=10 \mathrm{~ms}^{-2}$ )
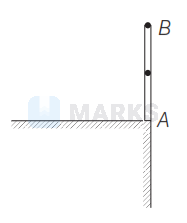
Options:

Solution:
1657 Upvotes
Verified Answer
The correct answer is:
$30 \mathrm{rads}^{-1}$
Given, length of $\operatorname{rod} A B, l=1 \mathrm{~m}$
Displacement of centre of mass, $s=5 \sqrt{2} \mathrm{~m}$
Time taken, $t=1 \mathrm{~s}$
Acceleration due to gravity, $g=10 \mathrm{~ms}^{-2}$
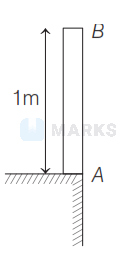
Let vertical displacement in $1 \mathrm{~s}=y$
Angular velocity $=\omega$
Moment of inertia $=I$
$I($ about centre of rod $)=m l^2 / 12$
$\because \quad y=u t+\frac{1}{2} g t^2$
$\therefore \quad y=\frac{1}{2} \times 10 \times 1^2=5 \mathrm{~m}$
and $\quad s=\sqrt{x^2+y^2}$
$\therefore \quad(5 \sqrt{2})^2=x^2+y^2$
$\Rightarrow \quad(5 \sqrt{2})^2=x^2+5^2$
Displacement along $X$-axis in 1s
$$
\begin{aligned}
& & x^2=50-25 \\
\Rightarrow & & x=\sqrt{25}=5 \mathrm{~m} \\
\therefore & & v_x=\frac{x}{t}=5 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}
\end{aligned}
$$
Since, angular impulse $=$ change in angular momentum
$$
\begin{aligned}
& & J \cdot l / 2 & =I \omega \\
\Rightarrow & & m v l / 2 & =\frac{m l^2}{12} \omega \\
\Rightarrow & & \omega & =6 \mathrm{v}=6 \times 5=30 \mathrm{rads}^{-1}
\end{aligned}
$$
Displacement of centre of mass, $s=5 \sqrt{2} \mathrm{~m}$
Time taken, $t=1 \mathrm{~s}$
Acceleration due to gravity, $g=10 \mathrm{~ms}^{-2}$

Let vertical displacement in $1 \mathrm{~s}=y$
Angular velocity $=\omega$
Moment of inertia $=I$
$I($ about centre of rod $)=m l^2 / 12$
$\because \quad y=u t+\frac{1}{2} g t^2$
$\therefore \quad y=\frac{1}{2} \times 10 \times 1^2=5 \mathrm{~m}$
and $\quad s=\sqrt{x^2+y^2}$
$\therefore \quad(5 \sqrt{2})^2=x^2+y^2$
$\Rightarrow \quad(5 \sqrt{2})^2=x^2+5^2$
Displacement along $X$-axis in 1s
$$
\begin{aligned}
& & x^2=50-25 \\
\Rightarrow & & x=\sqrt{25}=5 \mathrm{~m} \\
\therefore & & v_x=\frac{x}{t}=5 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}
\end{aligned}
$$
Since, angular impulse $=$ change in angular momentum
$$
\begin{aligned}
& & J \cdot l / 2 & =I \omega \\
\Rightarrow & & m v l / 2 & =\frac{m l^2}{12} \omega \\
\Rightarrow & & \omega & =6 \mathrm{v}=6 \times 5=30 \mathrm{rads}^{-1}
\end{aligned}
$$
Looking for more such questions to practice?
Download the MARKS App - The ultimate prep app for IIT JEE & NEET with chapter-wise PYQs, revision notes, formula sheets, custom tests & much more.