Search any question & find its solution
Question:
Answered & Verified by Expert
A straight line which makes equal intercepts on positive $X$ and $Y$ axes and which is at a distance 1 unit from the origin intersects the straight line $y=2 x+3+\sqrt{2}$ at $\left(x_0, y_0\right)$. Then $2 x_0+y_0$ is equal to
Options:
Solution:
1540 Upvotes
Verified Answer
The correct answer is:
$\sqrt{2}-1$
The equation of line $A B$ which makes an equal intercepts on positive $x$ and $y$ axes are
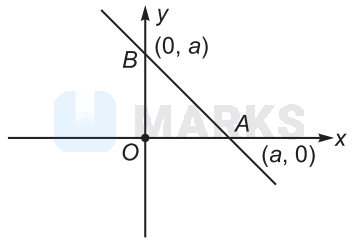
$\frac{x}{a}+\frac{y}{a}=1$
ie, $\quad x+y=a$ ...(i)
Distance of Eq. (i) from origin $=1$
$\left|\frac{0+0-a}{\sqrt{1+1}}\right|=1, \frac{-a}{\sqrt{2}} \mid=1$
$\Rightarrow \quad a=\sqrt{2}$
From Eq. (i), $\quad x+y=\sqrt{2}$ ...(ii)
Also given line,
$2 x-y=-3-\sqrt{2}$ ...(iii)
The intersection point of line (ii) and line (iii) is
$\left(x_0, y_0\right)=(-1, \sqrt{2}+1)$
So, $\quad 2 x_0+y_0=2(-1)+\sqrt{2}+1$
$=-2+\sqrt{2}+1=(\sqrt{2}-1)$
Hence, $\quad 2 x_0+y_0=\sqrt{2}-1$

$\frac{x}{a}+\frac{y}{a}=1$
ie, $\quad x+y=a$ ...(i)
Distance of Eq. (i) from origin $=1$
$\left|\frac{0+0-a}{\sqrt{1+1}}\right|=1, \frac{-a}{\sqrt{2}} \mid=1$
$\Rightarrow \quad a=\sqrt{2}$
From Eq. (i), $\quad x+y=\sqrt{2}$ ...(ii)
Also given line,
$2 x-y=-3-\sqrt{2}$ ...(iii)
The intersection point of line (ii) and line (iii) is
$\left(x_0, y_0\right)=(-1, \sqrt{2}+1)$
So, $\quad 2 x_0+y_0=2(-1)+\sqrt{2}+1$
$=-2+\sqrt{2}+1=(\sqrt{2}-1)$
Hence, $\quad 2 x_0+y_0=\sqrt{2}-1$
Looking for more such questions to practice?
Download the MARKS App - The ultimate prep app for IIT JEE & NEET with chapter-wise PYQs, revision notes, formula sheets, custom tests & much more.