Search any question & find its solution
Question:
Answered & Verified by Expert
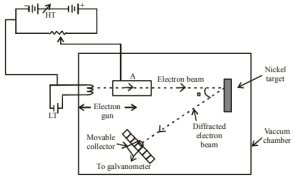
Consider figure given below. Suppose the voltage applied to $\mathrm{A}$ is increased. The diffracted beam will have the maximum at value of $\theta$ that
Options:

Solution:
2475 Upvotes
Verified Answer
The correct answer is:
will be less than the earlier value
will be less than the earlier value
We know that,
In Davisson - Germer experiment, the de-Broglie wavelength associated with electron is
$$
\lambda_{\mathrm{d}}=\frac{12.27}{\sqrt{\mathrm{V}}} Å
$$
where $V$ is the applied voltage. If there is a maxima of the diffracted electrons at an angle $\theta$, than
$2 d \sin \theta=\lambda$
..(ii)
From equation (i) if $\mathrm{V}$ is inversely proportional to the wavelength $\lambda_{\mathrm{d}}$, then the applied voltage $\mathrm{V}$ will increase with the decrease in the wavelengh $\lambda_{\mathrm{d}}$.
From equation (ii) if wavelength $\lambda_{\mathrm{d}}$ is directly proportional to $\sin \theta$ and hence $\theta$.
So, with the decrease in $\lambda_{\mathrm{d}} \sin \theta, \theta$ will also decrease. Hence, when the voltage applied to $\mathrm{A}$ is increased. The diffracted beam will have the maximum at a value of $\theta$ that will be less than the earlier value.
In Davisson - Germer experiment, the de-Broglie wavelength associated with electron is
$$
\lambda_{\mathrm{d}}=\frac{12.27}{\sqrt{\mathrm{V}}} Å
$$
where $V$ is the applied voltage. If there is a maxima of the diffracted electrons at an angle $\theta$, than
$2 d \sin \theta=\lambda$
..(ii)
From equation (i) if $\mathrm{V}$ is inversely proportional to the wavelength $\lambda_{\mathrm{d}}$, then the applied voltage $\mathrm{V}$ will increase with the decrease in the wavelengh $\lambda_{\mathrm{d}}$.
From equation (ii) if wavelength $\lambda_{\mathrm{d}}$ is directly proportional to $\sin \theta$ and hence $\theta$.
So, with the decrease in $\lambda_{\mathrm{d}} \sin \theta, \theta$ will also decrease. Hence, when the voltage applied to $\mathrm{A}$ is increased. The diffracted beam will have the maximum at a value of $\theta$ that will be less than the earlier value.
Looking for more such questions to practice?
Download the MARKS App - The ultimate prep app for IIT JEE & NEET with chapter-wise PYQs, revision notes, formula sheets, custom tests & much more.