Search any question & find its solution
Question:
Answered & Verified by Expert
If the area of the circle \(x^2+y^2=2\) is divided into two parts by the parabola \(y=x^2\), then the area (in sq units) of the larger part is
Options:
Solution:
2212 Upvotes
Verified Answer
The correct answer is:
\(\frac{3 \pi}{2}-\frac{1}{3}\)
Given equation of curves
\(x^2+y^2=2 \text { and } y=x^2\)
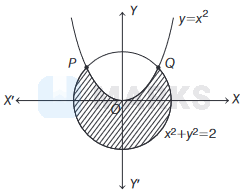
For point of intersection, on solving the given curves, we get
\(\begin{aligned}
& y^2+y-2=0 \Rightarrow y^2+2 y-y-2=0 \\
\Rightarrow & y(y+2)-1(y+2) =0 \\
\Rightarrow & y =1 \qquad {[\because y > 0] }
\end{aligned}\)
So, the required area
\(\begin{aligned}
& =\pi+2 \int_0^1\left(\sqrt{\left.2-y^2\right)}-\sqrt{y}\right) d y \\
& =\pi+2\left[\frac{y}{2} \sqrt{2-y^2}+\frac{2}{2} \sin ^{-1} \frac{y}{\sqrt{2}}-\frac{2}{3} y^{3 / 2}\right]_0^1 \\
& =\pi+2\left[\frac{1}{2}+\frac{\pi}{4}-\frac{2}{3}\right]=\frac{3 \pi}{2}+1-\frac{4}{3}
\end{aligned}\)
\(=\frac{3 \pi}{2}-\frac{1}{3} \text { sq. units }\)
Hence, option (1) is correct.
\(x^2+y^2=2 \text { and } y=x^2\)

For point of intersection, on solving the given curves, we get
\(\begin{aligned}
& y^2+y-2=0 \Rightarrow y^2+2 y-y-2=0 \\
\Rightarrow & y(y+2)-1(y+2) =0 \\
\Rightarrow & y =1 \qquad {[\because y > 0] }
\end{aligned}\)
So, the required area
\(\begin{aligned}
& =\pi+2 \int_0^1\left(\sqrt{\left.2-y^2\right)}-\sqrt{y}\right) d y \\
& =\pi+2\left[\frac{y}{2} \sqrt{2-y^2}+\frac{2}{2} \sin ^{-1} \frac{y}{\sqrt{2}}-\frac{2}{3} y^{3 / 2}\right]_0^1 \\
& =\pi+2\left[\frac{1}{2}+\frac{\pi}{4}-\frac{2}{3}\right]=\frac{3 \pi}{2}+1-\frac{4}{3}
\end{aligned}\)
\(=\frac{3 \pi}{2}-\frac{1}{3} \text { sq. units }\)
Hence, option (1) is correct.
Looking for more such questions to practice?
Download the MARKS App - The ultimate prep app for IIT JEE & NEET with chapter-wise PYQs, revision notes, formula sheets, custom tests & much more.