Search any question & find its solution
Question:
Answered & Verified by Expert
If the family of curves $y=a e^{4 x}+b e^{-x}$, where $a, b$ are arbitrary constants represents the general solution of the differential equation $f\left(x, y \frac{d y}{d x}, \frac{d^2 y}{d x^2}\right)=0$, then $\frac{d f}{d x}=$
Options:
Solution:
1380 Upvotes
Verified Answer
The correct answer is:
$\frac{d^3 y}{d x^3}-3 \frac{d^2 y}{d x^2}-4 \frac{d y}{d x}$
We have,
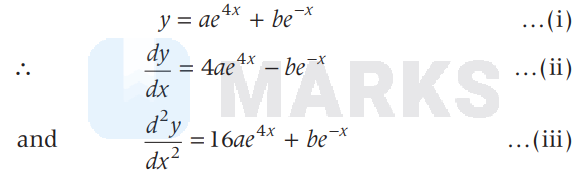
On adding Eqs. (i) and (ii), we get
$y+\frac{d y}{d x}=5 a e^{4 x}$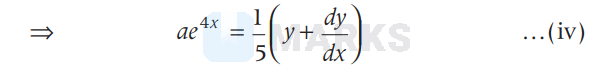
From Eqs. (i) and (iv), we get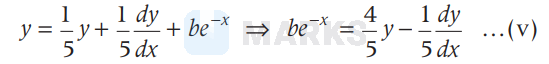
From Eqs. (iii), (iv) and (v), we get
$\frac{d^2 y}{d x^2}=\frac{16}{5} y+\frac{16}{5} \frac{d y}{d x}+\frac{4}{5} y-\frac{1}{5} \frac{d y}{d x}$
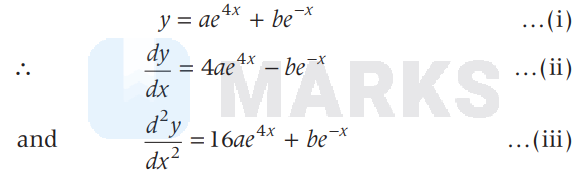
On adding Eqs. (i) and (ii), we get
$y+\frac{d y}{d x}=5 a e^{4 x}$
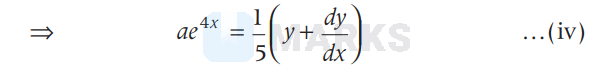
From Eqs. (i) and (iv), we get
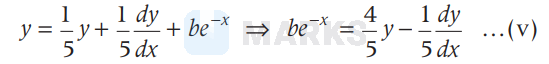
From Eqs. (iii), (iv) and (v), we get
$\frac{d^2 y}{d x^2}=\frac{16}{5} y+\frac{16}{5} \frac{d y}{d x}+\frac{4}{5} y-\frac{1}{5} \frac{d y}{d x}$
Looking for more such questions to practice?
Download the MARKS App - The ultimate prep app for IIT JEE & NEET with chapter-wise PYQs, revision notes, formula sheets, custom tests & much more.