Search any question & find its solution
Question:
Answered & Verified by Expert
In the circuit shown in figure, when the input voltage of the base resistance is $10 \mathrm{~V}, V_{b e}$ is zero and $V_{c e}$ is also zero. Value of $\beta$ is
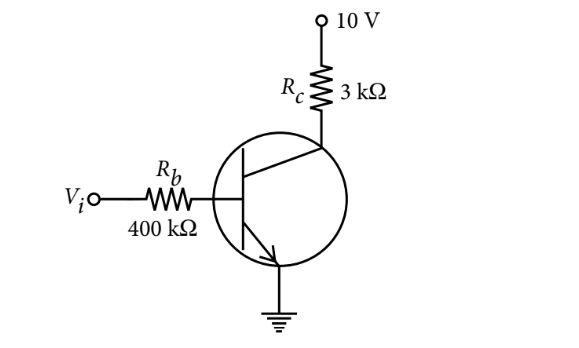
Options:

Solution:
1563 Upvotes
Verified Answer
The correct answer is:
$133$
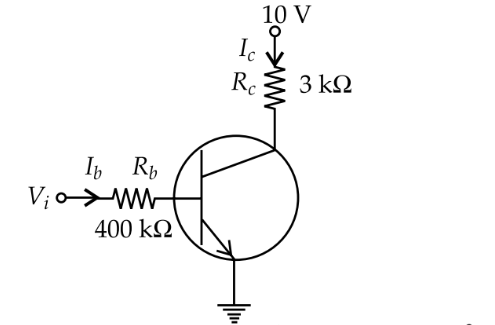
Given $V_i=10 \mathrm{~V}, R_b=\overline{\overline{ }} 00 \mathrm{k} \Omega=400 \times 10^3 \Omega$
$\begin{aligned} & R_c=3 \mathrm{k} \Omega=3 \times 10^3 \Omega, V_{b e}=0 \\ & V_{c e}=0, V_{C C}=10 \mathrm{~V} \\ & \text { As } V_i-V_{b e}=R_b I_b\end{aligned}$
$\begin{aligned} & \therefore \quad 10-0=\left(400 \times 10^3\right) I_b \\ & I_b=\frac{10}{400 \times 10^3}=25 \times 10^{-6} \mathrm{~A}=25 \mu \mathrm{A} \\ & \text { and } V_{C C}-V_{c e}=I_c R_c\end{aligned}$
$\begin{aligned} & I_c=\frac{10}{3 \times 10^3}=3.33 \times 10^{-3}=3.33 \mathrm{~mA} \\ & \beta=\frac{I_c}{I_b}=\frac{3.33 \times 10^{-3}}{25 \times 10^{-6}}=133\end{aligned}$
Looking for more such questions to practice?
Download the MARKS App - The ultimate prep app for IIT JEE & NEET with chapter-wise PYQs, revision notes, formula sheets, custom tests & much more.