Search any question & find its solution
Question:
Answered & Verified by Expert
The gravitational force acting on a particle, due to a solid sphere of uniform density and radius $R$, at a distance of $3 R$ from the centre of the sphere is $F_1$. A spherical hole of radius $(R / 2)$ is now made in the sphere as shown in the figure. The sphere with hole now exerts a force $F_2$ on the same particle. Ratio of $F_1$ and $F_2$ is
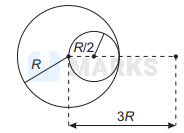
Options:

Solution:
2847 Upvotes
Verified Answer
The correct answer is:
$\frac{50}{41}$
Gravitational force due to solid sphere is
$$
F_1=\frac{G M m}{(3 R)^2}=\frac{G M m}{9 R^2}
$$
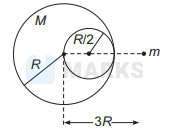
where, $M$ and $m$ are mass of solid sphere and particle respectively. Gravitational force on particle due to sphere with cavity
$$
\begin{aligned}
F_2 & =\frac{G M m}{9 R^2}-\frac{G\left(\frac{M}{8}\right) m}{(5 R / 2)^2} \\
& =\frac{G M m}{R^2}\left[\frac{1}{9}-\frac{4}{8 \times 25}\right] \\
& =\frac{G M m}{R^2}\left[\frac{41}{50 \times 9}\right] \\
\therefore \quad \frac{F_1}{F_2} & =\frac{50}{41}
\end{aligned}
$$
$$
F_1=\frac{G M m}{(3 R)^2}=\frac{G M m}{9 R^2}
$$

where, $M$ and $m$ are mass of solid sphere and particle respectively. Gravitational force on particle due to sphere with cavity
$$
\begin{aligned}
F_2 & =\frac{G M m}{9 R^2}-\frac{G\left(\frac{M}{8}\right) m}{(5 R / 2)^2} \\
& =\frac{G M m}{R^2}\left[\frac{1}{9}-\frac{4}{8 \times 25}\right] \\
& =\frac{G M m}{R^2}\left[\frac{41}{50 \times 9}\right] \\
\therefore \quad \frac{F_1}{F_2} & =\frac{50}{41}
\end{aligned}
$$
Looking for more such questions to practice?
Download the MARKS App - The ultimate prep app for IIT JEE & NEET with chapter-wise PYQs, revision notes, formula sheets, custom tests & much more.