Search any question & find its solution
Question:
Answered & Verified by Expert
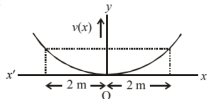
The potential energy function for a particle executing linear simple harmonic motion is given by $V(x)=\frac{1}{2} k x^2$, where $k$ is the force constant of the oscillator. For $k=0.5 \mathrm{~N} / \mathrm{m}$, the graph of $V(x)$ versus $x$ is shown in the figure. Show that a particle of total energy 1 joule moving under this potential must turn back, when it reaches $x=\pm 2 \mathrm{~m}$.
Solution:
1970 Upvotes
Verified Answer
At any instant, the total energy of an oscillator is equal to the sum of K.E. and P.E.
$$
E=\frac{1}{2} m v^2+\frac{1}{2} k x^2
$$
When $v=0$
$$
E=\frac{1}{2} k x^2 .
$$
At this instant the particle will comeback.
As $\mathrm{E}=1 \mathrm{~J}$ and $k=\frac{1}{2} N / m 1=\frac{1}{2} \times \frac{1}{2} x^2$
$$
\Rightarrow x^2=4 \Rightarrow x=\pm 2 \mathrm{~m}
$$
$$
E=\frac{1}{2} m v^2+\frac{1}{2} k x^2
$$

When $v=0$
$$
E=\frac{1}{2} k x^2 .
$$
At this instant the particle will comeback.
As $\mathrm{E}=1 \mathrm{~J}$ and $k=\frac{1}{2} N / m 1=\frac{1}{2} \times \frac{1}{2} x^2$
$$
\Rightarrow x^2=4 \Rightarrow x=\pm 2 \mathrm{~m}
$$
Looking for more such questions to practice?
Download the MARKS App - The ultimate prep app for IIT JEE & NEET with chapter-wise PYQs, revision notes, formula sheets, custom tests & much more.