Search any question & find its solution
Question:
Answered & Verified by Expert
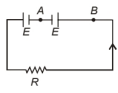
Two cells of same emfE but internal resistance $\mathrm{r}_1$ and $\mathrm{r}_2$ are connected in series to an external resistor $\mathrm{R}$ (figure). What should be the value of $R$ so that the potential difference across the terminals of the first cell becomes zero?

Solution:
2206 Upvotes
Verified Answer
Applying Ohm's law,
$$
V=\mathbb{R} \text {, }
$$
The Effective resistance $=\mathrm{R}+\mathrm{r}_1+\mathrm{r}_2$ and effective emf of two cells $=\mathrm{E}+\mathrm{E}=2 \mathrm{E}$, so the electric current I following in the circuit is
$$
\mathrm{I}=\frac{\mathrm{E}+\mathrm{E}}{\mathrm{R}+\mathrm{r}_1+\mathrm{r}_2}
$$
The net potential difference across the terminals of the 1st cell and putting it equal to zero.
$$
\begin{aligned}
&\begin{aligned}
\mathrm{V}_1 &=\mathrm{E}-\mathrm{Ir}_1 \quad\left(\because \mathrm{V}_1=0\right) \text { given } \\
&=\mathrm{E}-\frac{2 \mathrm{E}}{\mathrm{r}_1+\mathrm{r}_2+\mathrm{R}} \mathrm{r}_1=0 \\
\text { or, } \quad \mathrm{E} &=\frac{2 E \mathrm{E}_1}{\mathrm{r}_1+\mathrm{r}_2+\mathrm{R}} \\
1 &=\frac{2 \mathrm{r}_1}{\mathrm{r}_1+\mathrm{r}_2+\mathrm{R}} \\
\text { or, } \mathrm{r}_1+\mathrm{r}_2+\mathrm{R}=2 \mathrm{r}_1 \\
\mathrm{R}=\mathrm{r}_1-\mathrm{r}_2
\end{aligned}
\end{aligned}
$$
This is the required condition for the potential difference across 1st cell to be zero.
$$
V=\mathbb{R} \text {, }
$$
The Effective resistance $=\mathrm{R}+\mathrm{r}_1+\mathrm{r}_2$ and effective emf of two cells $=\mathrm{E}+\mathrm{E}=2 \mathrm{E}$, so the electric current I following in the circuit is
$$
\mathrm{I}=\frac{\mathrm{E}+\mathrm{E}}{\mathrm{R}+\mathrm{r}_1+\mathrm{r}_2}
$$
The net potential difference across the terminals of the 1st cell and putting it equal to zero.
$$
\begin{aligned}
&\begin{aligned}
\mathrm{V}_1 &=\mathrm{E}-\mathrm{Ir}_1 \quad\left(\because \mathrm{V}_1=0\right) \text { given } \\
&=\mathrm{E}-\frac{2 \mathrm{E}}{\mathrm{r}_1+\mathrm{r}_2+\mathrm{R}} \mathrm{r}_1=0 \\
\text { or, } \quad \mathrm{E} &=\frac{2 E \mathrm{E}_1}{\mathrm{r}_1+\mathrm{r}_2+\mathrm{R}} \\
1 &=\frac{2 \mathrm{r}_1}{\mathrm{r}_1+\mathrm{r}_2+\mathrm{R}} \\
\text { or, } \mathrm{r}_1+\mathrm{r}_2+\mathrm{R}=2 \mathrm{r}_1 \\
\mathrm{R}=\mathrm{r}_1-\mathrm{r}_2
\end{aligned}
\end{aligned}
$$
This is the required condition for the potential difference across 1st cell to be zero.
Looking for more such questions to practice?
Download the MARKS App - The ultimate prep app for IIT JEE & NEET with chapter-wise PYQs, revision notes, formula sheets, custom tests & much more.