Search any question & find its solution
Question:
Answered & Verified by Expert
If $Q$ is the inverse point of the point $\mathrm{P}(2,3)$ with respect to the circle $x^2+y^2-2 x-2 y+1=0$, then the circle with $\mathrm{PQ}$ as diameter is
Options:
Solution:
1093 Upvotes
Verified Answer
The correct answer is:
$5 x^2+5 y^2-16 x-22 y+33=0$
Let the co-ordinate of the point $Q$ is $(h, k)$.
Equation of line $O P$ :
$(y-3)=\frac{2}{1}(x-1)$
$\Rightarrow \quad 2 x-y=1$ ...(1)
$\because(h, k)$ is on the line $O P$
$\therefore \quad 2 h-k=1 \Rightarrow k=2 h-1$
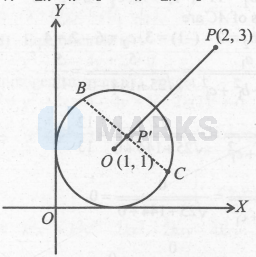
So, co-ordinate of $P$ is $(h, 2 h-1)$.
Also, $O P \times O Q=r^2$
$\begin{aligned} & \Rightarrow \sqrt{1+4} \times O Q^{\prime}=r^2 \Rightarrow O Q=\frac{1}{\sqrt{5}} \\ & \Rightarrow \sqrt{(h-1)^2+(2 h-1-1)^2}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{5}}\end{aligned}$
$\begin{aligned} & \Rightarrow \quad 25 h^2-50 h+24=0 \\ & \Rightarrow \quad h=\frac{6}{5}, \frac{4}{5}\end{aligned}$
Let $h=\frac{6}{5}$. Then $k=2 \times \frac{6}{5}-1=\frac{7}{5}$
Then $Q=\left(\frac{6}{5}, \frac{7}{5}\right)$.
Eqn. of line with $P Q$ as diameter is
$\begin{aligned} & (x-2)\left(x-\frac{6}{5}\right)+(y-3)\left(y-\frac{7}{5}\right)=0 \\ & \Rightarrow \quad(x-2)(5 x-6)+(5 y-7)(y-3)=0 \\ & \Rightarrow 5 x^2+5 y^2-6 x-22 y+33=0 .\end{aligned}$
Equation of line $O P$ :
$(y-3)=\frac{2}{1}(x-1)$
$\Rightarrow \quad 2 x-y=1$ ...(1)
$\because(h, k)$ is on the line $O P$
$\therefore \quad 2 h-k=1 \Rightarrow k=2 h-1$

So, co-ordinate of $P$ is $(h, 2 h-1)$.
Also, $O P \times O Q=r^2$
$\begin{aligned} & \Rightarrow \sqrt{1+4} \times O Q^{\prime}=r^2 \Rightarrow O Q=\frac{1}{\sqrt{5}} \\ & \Rightarrow \sqrt{(h-1)^2+(2 h-1-1)^2}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{5}}\end{aligned}$
$\begin{aligned} & \Rightarrow \quad 25 h^2-50 h+24=0 \\ & \Rightarrow \quad h=\frac{6}{5}, \frac{4}{5}\end{aligned}$
Let $h=\frac{6}{5}$. Then $k=2 \times \frac{6}{5}-1=\frac{7}{5}$
Then $Q=\left(\frac{6}{5}, \frac{7}{5}\right)$.
Eqn. of line with $P Q$ as diameter is
$\begin{aligned} & (x-2)\left(x-\frac{6}{5}\right)+(y-3)\left(y-\frac{7}{5}\right)=0 \\ & \Rightarrow \quad(x-2)(5 x-6)+(5 y-7)(y-3)=0 \\ & \Rightarrow 5 x^2+5 y^2-6 x-22 y+33=0 .\end{aligned}$
Looking for more such questions to practice?
Download the MARKS App - The ultimate prep app for IIT JEE & NEET with chapter-wise PYQs, revision notes, formula sheets, custom tests & much more.