Search any question & find its solution
Question:
Answered & Verified by Expert
Let $A(4,3,5), B(1,-2,1), C(3,2,1)$ be the vertices of a triangle $\mathrm{ABC}$. If the internal bisector of $\angle \mathrm{BAC}$ meet the side $\mathrm{BC}$ at $\mathrm{D}$, then $\mathrm{CD}=$
Options:
Solution:
2968 Upvotes
Verified Answer
The correct answer is:
$\frac{3 \sqrt{5}}{4}$
$$
\begin{aligned}
A B= & \sqrt{3^2+5^2+4^2}=5 \sqrt{2} \\
A C= & \sqrt{1^2+1^2+4^2}=3 \sqrt{2} \\
& \frac{A B}{A C}=\frac{B D}{D C} \\
\Rightarrow & \frac{5 \sqrt{2}}{3 \sqrt{2}}=\frac{B D}{D C}=\frac{5}{3}
\end{aligned}
$$
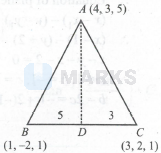
$\therefore$ Co-ordinates of $D$ are:
$$
\begin{aligned}
x= & \frac{15+3}{8}=\frac{9}{4} ; y=\frac{10-6}{8}=\frac{1}{2} \text { and } z=\frac{5+3}{8}=1 \\
\therefore D C & =\sqrt{(x-3)^2+(y-2)^2+(z-1)^2} \\
& =\sqrt{\left(\frac{9}{4}-3\right)^2+\left(\frac{1}{2}-2\right)^2+(1-1)^2} \\
& =\sqrt{\frac{9}{16}+\frac{9}{4}}=\sqrt{\frac{45}{16}}=\frac{3 \sqrt{5}}{4} .
\end{aligned}
$$
\begin{aligned}
A B= & \sqrt{3^2+5^2+4^2}=5 \sqrt{2} \\
A C= & \sqrt{1^2+1^2+4^2}=3 \sqrt{2} \\
& \frac{A B}{A C}=\frac{B D}{D C} \\
\Rightarrow & \frac{5 \sqrt{2}}{3 \sqrt{2}}=\frac{B D}{D C}=\frac{5}{3}
\end{aligned}
$$

$\therefore$ Co-ordinates of $D$ are:
$$
\begin{aligned}
x= & \frac{15+3}{8}=\frac{9}{4} ; y=\frac{10-6}{8}=\frac{1}{2} \text { and } z=\frac{5+3}{8}=1 \\
\therefore D C & =\sqrt{(x-3)^2+(y-2)^2+(z-1)^2} \\
& =\sqrt{\left(\frac{9}{4}-3\right)^2+\left(\frac{1}{2}-2\right)^2+(1-1)^2} \\
& =\sqrt{\frac{9}{16}+\frac{9}{4}}=\sqrt{\frac{45}{16}}=\frac{3 \sqrt{5}}{4} .
\end{aligned}
$$
Looking for more such questions to practice?
Download the MARKS App - The ultimate prep app for IIT JEE & NEET with chapter-wise PYQs, revision notes, formula sheets, custom tests & much more.