Search any question & find its solution
Question:
Answered & Verified by Expert
$O A$ and $O B$ are two roads enclosing an angle of $120^{\circ} . X$ and $Y$ start from ' $O$ ' at the same time. $X$ travels along $O A$ with a speed of $4 \mathrm{~km} / \mathrm{h}$ and $Y$ travels along $O B$ with a speed of $3 \mathrm{~km} / \mathrm{h}$. The rate at which the shortest distance between $X$ and $Y$ is increasing after $1 \mathrm{~h}$ is
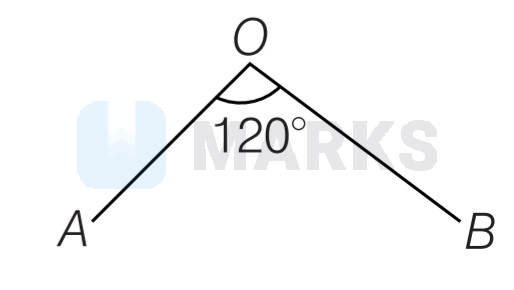
Options:

Solution:
2642 Upvotes
Verified Answer
The correct answer is:
$\sqrt{37} \mathrm{~km} / \mathrm{h}$
Given, speed of $x$ is $4 \mathrm{~km} / \mathrm{h}$ and $y$ is $3 \mathrm{~km} / \mathrm{h}$. After time $t$ the distance covered by $x$ is $4 t$ and $y$ is $3 t$.
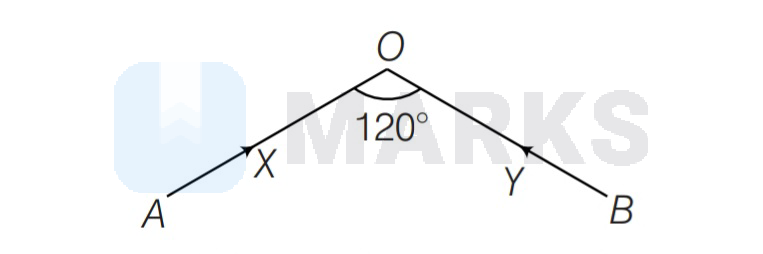
Let shortest distance between $x$ and $y=A$.
Then by cosine law
$\quad A^{2}=(4 t)^{2}+(3 t)^{2}-(4 t)(3 t) 2 \cos 120^{\circ}$ $\Rightarrow \quad A^{2}=16 t^{2}+9 t^{2}-24 t^{2}\left(-\frac{1}{2}\right)$ $\Rightarrow \quad A^{2}=25 t^{2}+12 t^{2}$ $\Rightarrow \quad A^{2}=37 t^{2}$ $\Rightarrow \quad A=\sqrt{37} t$ If $\quad t=1 \mathrm{~h}$, then $\quad A=\sqrt{37} \mathrm{~km}$ Now, differentiating Eq. (i) w.r.t. $t$, we get $\quad 2 A A^{\prime}=37(2 t)$ After $t=1 \mathrm{~h}$, we get $2 \sqrt{37} A^{\prime}=2(37)$
After $t=1 \mathrm{~h}$, we get
$\Rightarrow \quad A^{\prime}=\sqrt{37}$
Thus, rate at which shortest distance $A$ changes with time is $\sqrt{37} \mathrm{~km} / \mathrm{h}$.

Let shortest distance between $x$ and $y=A$.
Then by cosine law
$\quad A^{2}=(4 t)^{2}+(3 t)^{2}-(4 t)(3 t) 2 \cos 120^{\circ}$ $\Rightarrow \quad A^{2}=16 t^{2}+9 t^{2}-24 t^{2}\left(-\frac{1}{2}\right)$ $\Rightarrow \quad A^{2}=25 t^{2}+12 t^{2}$ $\Rightarrow \quad A^{2}=37 t^{2}$ $\Rightarrow \quad A=\sqrt{37} t$ If $\quad t=1 \mathrm{~h}$, then $\quad A=\sqrt{37} \mathrm{~km}$ Now, differentiating Eq. (i) w.r.t. $t$, we get $\quad 2 A A^{\prime}=37(2 t)$ After $t=1 \mathrm{~h}$, we get $2 \sqrt{37} A^{\prime}=2(37)$
After $t=1 \mathrm{~h}$, we get
$\Rightarrow \quad A^{\prime}=\sqrt{37}$
Thus, rate at which shortest distance $A$ changes with time is $\sqrt{37} \mathrm{~km} / \mathrm{h}$.
Looking for more such questions to practice?
Download the MARKS App - The ultimate prep app for IIT JEE & NEET with chapter-wise PYQs, revision notes, formula sheets, custom tests & much more.